INDONESIA
BACKGROUND AND CONTEXT
Since 2000, Indonesia has faced violent extremism, including international terrorism and domestic militant activity, with major incidents like the 2002 Bali bombings. After a period of calm, ISISinspired attacks resurfaced in 2016, though no terrorist attacks occurred from 2023 to 2025. Despite this, extremist recruitment and activities persist. Jemaah Islamiyah (JI), a key VE organisation, officially disbanded on June 30, 2024, with over 2,400 members renouncing ties and pledging allegiance to the government. However, experts warn of splinter groups, and the continued arrests of extremists highlight ongoing risks of radicalisation and terrorism.
In Indonesia, the drivers behind violent extremism are: extreme religious interpretations, poverty and economic exclusion, electoral polarisation and alienation, gaps of moderate religious organisations and online radicalisation. GCERF began investing in the country in 2025 and till date USD 2.3 million has been invested to address these drivers of violent extremism.
OUR INVESTMENT STRATEGY IN INDONESIA
GCERF’s investment strategy outlines a comprehensive approach to address the drivers of violent extremism and guides civil society organisations in designing their programmes.
To achieve these objectives, GCERF funds programmes that:
Support rehabilitation and reintegration of people from conflict areas
Support integration of former detainees released from prison
Address online and offline radicalisation in formal and informal educational institutions
KEY FIGURES
(cumulative from 2021 to March 2025)
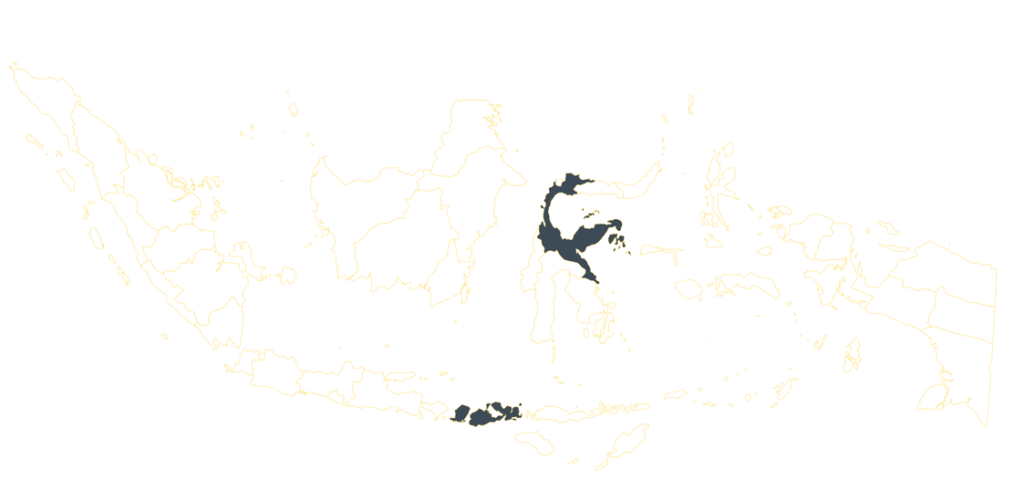
AREAS WHERE WE WORK
West Nusa Tenggara, Central Sulawesi, Jakarta
Newsletter

Sustainable Development Goals
Peace, Justice & Strong Institution
No Poverty
Quality Education
Gender Equality

Decent Work & Economic Growth

Reduced Inequalities

